View full image
Standard Model of Particle Physics Part 1
With an introduction of almost all the properties and natures of every subatomic particle would be described in this series. There would be more than 10 parts in this explanation series.
Series 1
Standard Model of Particle Physics
Disclaimer: The topic of this series is directly connected with Quantum Mechanics. So, in the whole series where the word 'Particle' would be used it would mean both 𝒘𝒂𝒗𝒆 and 𝒑𝒂𝒓𝒕𝒊𝒄𝒍𝒆 according to the fundamental laws of Quantum Mechanics.
𝗣𝗮𝗿𝘁-1
𝗜𝗻𝘁𝗿𝗼𝗱𝘂𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗼𝗳 𝗦𝘁𝗮𝗻𝗱𝗮𝗿𝗱 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹:
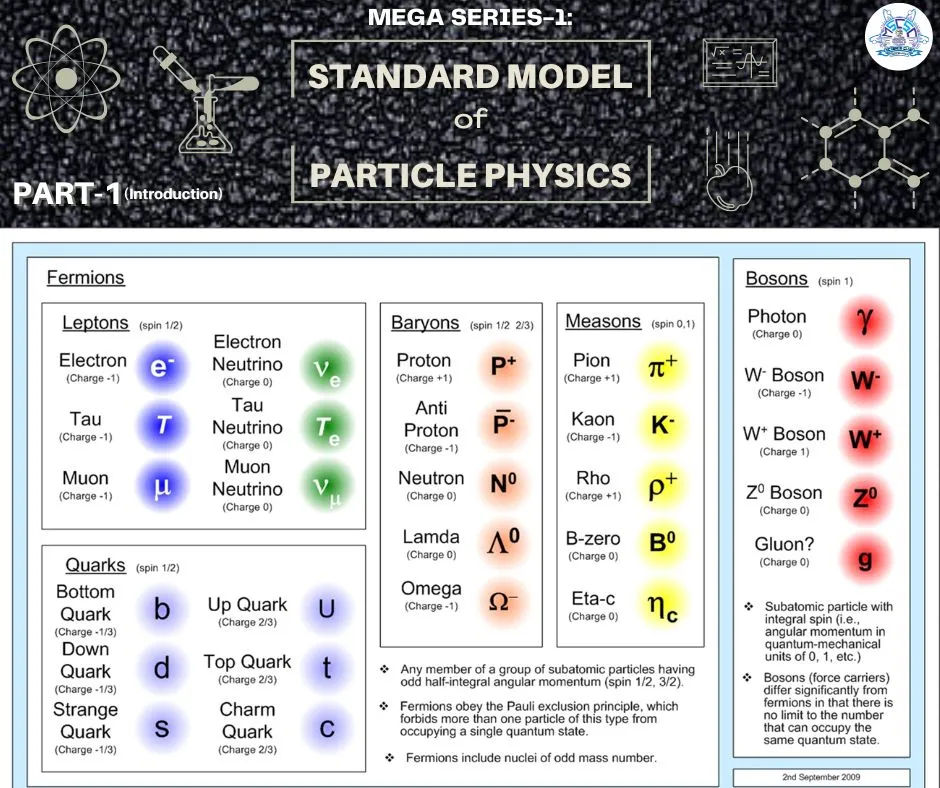
All matter in this universe is made up of tiny particles. Usually, our domestic textbooks only discuss electrons, protons, and neutrons, but usually what these three particles are made up of or what particles smaller than these are in the universe? It is not discussed. However, there are various types of small particles in the universe that control and carry all the fundamental forces of the universe as well as all the properties of matter. To facilitate work and research on all the fundamental particles of the universe, they have been included in a standard model. This model is called the "Standard Model". It is called the 'Model of Particle Physics'. Subatomic particles can be divided into different categories based on their 4 properties, and through these, all the properties of matter and the fundamental forces can be explained. These 4 properties are:
Spin or rotation of the particles
Electrical charge
Mass
Lifetime
Based on these properties, elementary particles can be divided into two main categories. These are:
Fermions (fermions)
Bosons 𝑩𝒐𝒔𝒐𝒏𝒔)
Fermions are mainly responsible for the creation of matter and bosons are mainly responsible for the creation of molecular forces
Classification of Fermions (𝗖𝗹𝗮𝘀𝘀𝗶𝗳𝗶𝗰𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗼𝗳 𝗙𝗲𝗿𝗺𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀):
Fermions are basically divided into two categories. These are:
Quarks (𝑸𝒖𝒂𝒓𝒌)
Leptons (𝑳𝒆𝒑𝒕𝒐𝒏𝒔)
Quarks There are a total of 6 types of electrons and 4 types of leptons.
Since quarks are unstable in nature, they combine with each other to achieve stability and form hadrons (𝑯𝒂𝒅𝒓𝒐𝒏𝒔),
Hadrons are divided into two types based on their composition: mesons (𝑴𝒆𝒔𝒐𝒏𝒔) and baryons (𝑩𝒂𝒓𝒚𝒐𝒏𝒔).
Classification of Bosons (𝗖𝗹𝗮𝘀𝘀𝗶𝗳𝗶𝗰𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗼𝗳 𝗕𝗼𝘀𝗼𝗻𝘀):
Bosons They are basically divided into 4 parts. These are:
Photons (𝑷𝒉𝒐𝒕𝒐𝒏𝒔)
W/Z bosons (𝑾/𝒁 𝑩𝒐𝒔𝒐𝒏𝒔)
Gluons (𝑮𝒍𝒖𝒐𝒏𝒔)
Gravitons (𝑮𝒓𝒂𝒗𝒊𝒕𝒐𝒏𝒔) (theoretically proven)
These four types of bosons are respectively electromagnetic force, weak nuclear force , responsible for the creation of the strong nuclear force and the gravitational force.
This is the initial introduction to the Standard Model.
(In the following parts, fermions and bosons and their classifications will be discussed in detail in stages. The next part will be uploaded every day.)